IDV Article
Biometric methods: Streamlined biometric authentication for seamless operations
Today, biometric data is used for a variety of purposes. In fact, most people use biometrics in their everyday lives. For example, if you use a smartphone, then you’ll already be using your biometric data for verification purposes multiple times a day.
Understanding the widespread adoption and importance of biometric methods
According to the Biometrics Institute, biometrics refers to the “automated recognition of individuals based on their biological and behavioral characteristics.” Biometrics are a way of measuring a person’s physical characteristics or quantifying their behavior. Each piece of biometric data a person possesses (such as a fingerprint or an iris scan), is unique. For this reason, when biometric identifiers are used, an individual’s identity can be accurately verified.
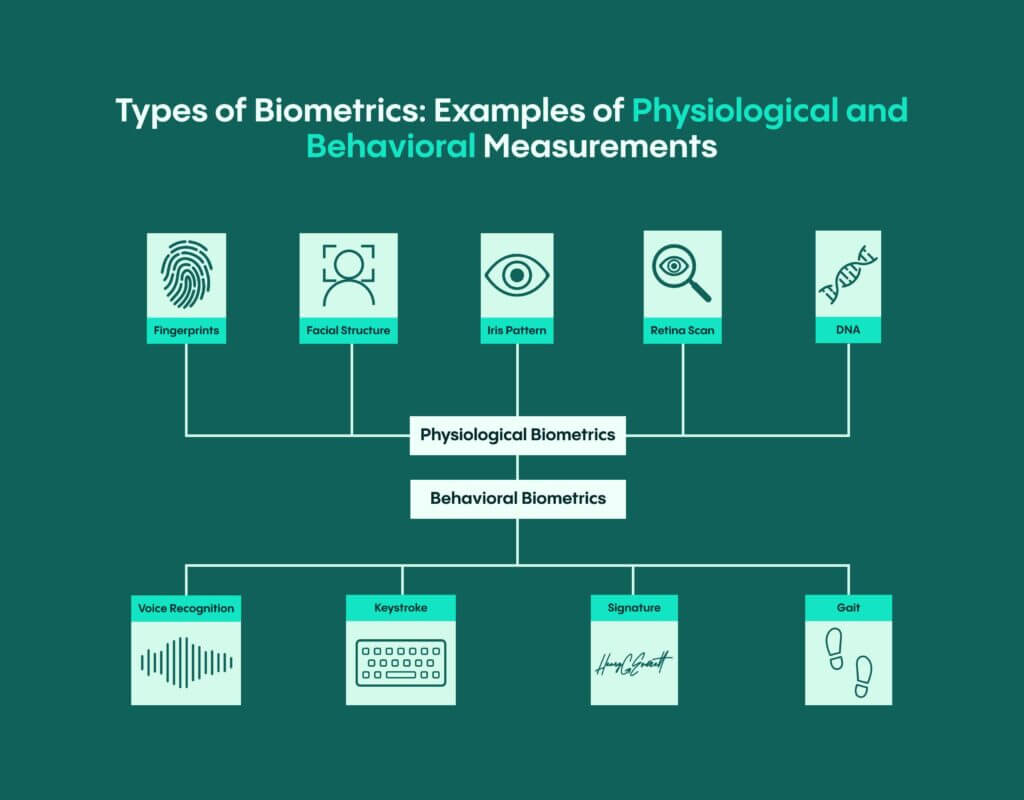
Although biometrics are a modern way of identifying and verifying a customer’s identity, their use is already widespread – having become one of the most popular and secure authentication methods. This is because biometrics provides a great deal of security for businesses while also increasing convenience for customers, who as a result of biometrics will no longer need to remember complex passwords.
The financial services sector has been at the forefront of adopting biometric technologies in the last decade. This shift is driven by competitive banking and payment players focusing on convenience and user experience, as well as regulatory requirements like KYC and AML promoting widespread identity verification during customer onboarding. Notably, applications in international money transfers and cryptocurrency wallet account recovery demand top-tier identity assurance through advanced matching and liveness technology. Healthcare is also entering this space due to the crucial need for precise patient identity data, despite facing challenges in cost and implementation. Governments, pivotal in establishing citizen identities, are embracing remote digital onboarding innovations to lead in biometric digital identity using mobile biometrics, liveness detection, and document validation. Educating decision-makers on the benefits and practicality of these technologies is key to achieving broad adoption in this sector.
How Veriff helps prevent ATO fraud
If your business is still using legacy authentication, your security measures are probably less sophisticated than the methods being used by fraudsters to try to access your clients’ accounts. As a business, you should assume bad actors know the limits of your approach to security and work with that as your baseline.
In the realm of high-value transactions, the need for robust security measures is paramount. Account takeover (ATO) fraud stands as a prominent peril confronting online enterprises in the current landscape. This nefarious activity not only poses significant financial risks to businesses but also places excessive strain on IT and customer service departments while also potentially tarnishing the company’s reputation. Given these ramifications, fraud detection has emerged as a paramount focus for organizations worldwide.
At Veriff, we’re proud to offer a range of class-leading solutions that can help you secure user accounts and lock out bad actors. Our identity verification solution and AML Screening solution can help you verify new users at onboarding, while our biometric authentication solution can be used to authenticate returning users and prevent account takeover fraud. This solution is much more reliable than passwords and one-time passcodes and is perfect for securing user accounts. It also allows you to lock fraudsters out of an account before they can change a customer’s details or attempt to make a purchase.
Passive liveness detection techniques are crucial, with Veriff ensuring the authenticity of end users effortlessly. Our system verifies the user’s presence without the need for extra actions. Moreover, our liveness models can identify fake attempts like mask presentation attacks or AI-generated selfies.
We also use face matching with AI to compare biometric templates from the authentication session to the stored biometric template from the enrolment session, confirming user identity.

With biometric authentication product we are on a mission to establish a new level of trust by authenticating users promptly and securely across all stages of the user journey with a single selfie.
Delving deeper into Veriff’s Biometric Authentication
At Veriff, we understand that organizations need to securely authenticate users without disrupting the user experience. This applies across the entire user journey, particularly at critical steps such as account access, undertaking a high-risk activity, and recovering an account. Veriff’s Biometric Authentication solution examines a user’s submitted selfie with AI-powered algorithms and facial biometric analysis – to instantly and securely authenticate previously verified users. making the moments that matter to your customers as seamless and stress-free as possible.
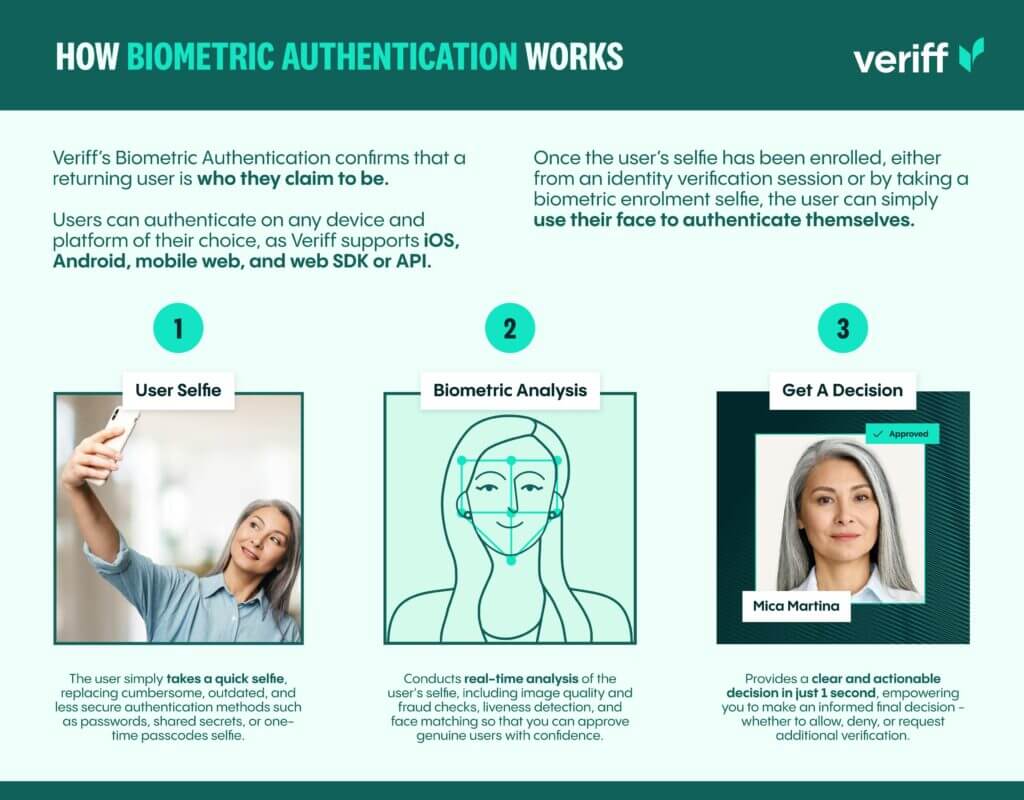
How Biometric Authentication works
Veriff’s Biometric Authentication confirms that a returning user is who they claim to be. Users can authenticate on any device and platform, as Veriff supports iOS, Android, mobile web, and web SDK or API.
Once the user’s selfie has been enrolled, either from an identity verification session or by taking a biometric enrolment selfie, the user can simply use their face to authenticate themselves.
Veriff’s biometric authentication confirms that a returning user is who they claim to be. Users can authenticate on any device and platform of their choice, as Veriff supports iOS, Android, mobile web, and web SDK or API. Once the user’s selfie has been enrolled, either from an identity verification session or by taking a biometric enrolment selfie, the user can use their face to authenticate themselves.
- User selfie
The user simply takes a quick selfie, replacing cumbersome, outdated, and less secure authentication methods such as passwords, shared secrets, or one-time passcodes selfie. - Biometric analysis
Conducts real-time analysis of the user’s selfie, including image quality and fraud checks, liveness detection, and face matching – so that you can approve genuine users with confidence. - Get a decision
Provides a clear and actionable decision in just one second, empowering you to make an informed final decision – whether to allow, deny, or request additional verification.
Case study analysis: Juancho te Presta’s partnership with Veriff
In the realm of fintech, where security and trust are paramount, the collaboration between Veriff and Juancho Te Presta has brought about a new era of biometric authentication that is redefining how financial services are accessed and utilized.
Juancho Te Presta stands as a beacon of financial empowerment in Colombia, catering to a diverse range of individuals, including employees, pensioners, students, and gig workers. Their commitment to using cutting-edge technology to facilitate quick and easy access to financial products underscores their dedication to helping people progress and achieve their aspirations. Notably, the company’s focus on the underserved female community in Colombia demonstrates a proactive approach toward promoting financial inclusion and gender equality within the financial landscape.
Veriff, renowned for its expertise in identity verification and biometric authentication, stepped in to address a crucial business problem for Juancho Te Presta. By leveraging Veriff’s state-of-the-art biometric authentication technology, Juancho Te Presta was able to enhance security measures, streamline the authentication process, and significantly reduce the risk of identity fraud. This collaboration not only ensured a seamless user experience but also instilled confidence in customers by providing them with a robust and trustworthy authentication mechanism.
As Juan Esteban Saldarriaga, founder and CEO of Juancho Te Presta, explained: “Previously, we were working with a different provider in order to help with our verification processes. But as our business grew, we realised we needed to be able to lean on a company that could offer an all-in-one solution.”
Their overall desire was to lower their number of fraud cases, meet compliance regulations and prevent lost revenue.

Biometric authentication, which helps us to automatically check if a new user is already on our system under another account, is one of the most powerful Veriff tools that we use.

