IDV Article
AML screening vs. transaction monitoring: A guide to compliance
Financial crime is evolving fast — fueled by AI, deepfakes, and smarter fraudsters. Staying compliant means staying one step ahead. Discover how AML screening and transaction monitoring work together to protect your business and your customers.
Financial crime is evolving at a staggering pace. As bad actors adopt sophisticated tools like AI and deepfakes, businesses face immense pressure to strengthen their defenses. A crucial part of this defense is a robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) framework, which hinges on two distinct but related processes: AML screening and AML transaction monitoring.
Understanding the difference between these two components is vital for any organization, especially those in financial services, to maintain compliance and protect their platforms from illicit activities. This post will break down AML screening vs. transaction monitoring, explain why both are essential, and show how modern identity verification technology is critical to getting them right.
What is AML screening?
AML screening (Anti-Money Laundering screening) is a process used by financial institutions and regulated businesses to identify and prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes. It involves checking individuals and entities against various watchlists, sanctions lists, politically exposed persons (PEP) databases, and adverse media sources.
This initial check involves cross-referencing a customer’s information against several critical lists, including:
- Sanctions lists: These are lists of individuals, entities, or countries that are subject to economic sanctions by governments or international bodies (e.g., OFAC, UN, EU lists).
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) lists: These identify individuals who hold prominent public functions and may pose a higher risk for potential bribery or corruption.
- Adverse media: This involves searching for negative news or reports about a potential customer, as well as checking internal watchlists, to identify possible involvement in financial crime or other reputational risks.
The goal of AML screening is to identify high-risk individuals or entities before they enter your ecosystem. If a person appears on a sanctions list, you are prohibited from doing business with them. However, if they are listed as a politically exposed person (PEP), you may still proceed but must apply enhanced due diligence and additional controls, as they pose a higher risk than the average customer. Effective AML screening not only helps businesses comply with regulations but also protects them from fines, reputational damage, loss of operating licenses, and increased regulatory scrutiny.

What is AML monitoring?
If screening is the gatekeeper, AML monitoring is the continuous review that happens once a customer has been onboarded. Also known as transaction monitoring, this process involves closely observing both historical and current customer transactions so you can build a comprehensive view of their activity over time. The goal? Spot and address suspicious behavior that might indicate money laundering, counter terrorist financing or other financial crimes before it causes harm to your business.
How does AML transaction monitoring work?
AML transaction monitoring refers to reviewing customer transactions across accounts, products, and services to detect potentially suspicious or high-risk activities. This process is rarely performed manually due to the immense volume and complexity of data involved. Instead, most financial institutions use specialized transaction monitoring software, which automates the review, applies detection rules, and quickly flags possible red flags.
Monitoring isn’t just about sifting through transactions randomly. It involves a rules-based system, where financial institutions set specific parameters according to their risk appetite, the nature of their business, and regulatory requirements. For example, thresholds might be established for unusually large transactions, sudden changes in transaction frequency or volume, dealing with high-risk jurisdictions, or attempts to structure deposits just below reporting limits. When a transaction triggers a rule, the transaction is flagged for further investigation. If the compliance or risk team believes the transaction is linked to criminal activity, it must be reported to the appropriate regulatory body by filing a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR).
Why is AML monitoring important?
AML monitoring is not a new requirement; it has long been a cornerstone of financial regulation. In the U.S., the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) has governed transaction reporting, suspicious activity reporting, and recordkeeping obligations for decades. Over time, these rules have evolved and been reinforced by subsequent laws, such as the USA PATRIOT Act, to address emerging threats. Our previous blog on the BSA outlines how these regulations continue to shape institutions today, influencing how compliance programs must adapt in a rapidly changing risk landscape.
Effective AML monitoring, spanning transactions, customer behavior, and risk profiles, helps prevent illicit funds from flowing through your business, safeguards your reputation, and shields you from penalties. In serious violation cases, fines can exceed $200 million, and institutions may also face loss of license or heightened regulatory scrutiny.
👉 To explore how the BSA impacts financial institutions in practice, see this in-depth article from Veriff: “Understanding the Bank Secrecy Act: Impact on Financial Institutions.”
The role of KYC in AML monitoring
AML transaction monitoring works hand-in-hand with Know Your Customer (KYC) processes. Data gathered at onboarding, such as customer identity, risk profile, and expected transaction behavior enables monitoring systems to set rules, define thresholds, and build a risk-based approach. These rules are continually updated as customer behavior and the risk landscape evolve, meaning the process is dynamic and adaptive. An accurate, up-to-date KYC baseline is essential for effective monitoring.
Best practices in AML transaction monitoring
While regulations mandate monitoring, they aren’t prescriptive about how you should do it. That’s why each business needs a carefully tailored approach based on its size, scale, risk exposure, and resources. Here are the key best practices:
- Automate where possible: Manual review is time-consuming and prone to error. Using modern software dramatically increases efficiency and accuracy.
- Blend automation with human oversight: Effective programs use automated tools for detection and rely on skilled compliance professionals to interpret complex scenarios, update rules, and review alerts.
- Define and update detection rules: Regularly review and update monitoring thresholds and detection parameters to reflect new risks, products, and regulations.
- Provide ongoing training: Ensure staff are trained to identify red flags—such as unusual client behavior, vague explanations about sources of funds, or overly complex business structures.
- Document your approach: Keep clear records of your policies, procedures, and changes made. This transparency is essential to demonstrate compliance to regulators.
- Ensure regular audits and reporting: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your systems, carry out internal audits, and report findings to management.

Common red flags in transaction monitoring
Red flags can include, but are not limited to:
- Clients changing advisors frequently without clear reasons.
- Requests for rushed or shortcut processes.
- Large transactions with unknown or inconsistent sources of funds.
- Businesses with overly complex ownership structures.
- Transactions involving high-risk countries or industries.
- Vague or incomplete information about the parties involved.
One red flag may warrant further investigation, but the presence of several together can indicate a much bigger issue.
The value of AML transaction monitoring tools
Modern transaction monitoring software not only streamlines compliance, but also offers evidence to regulators of your organization’s commitment to fighting financial crime. Automated solutions reduce manual workload, adapt quickly to changing risks, and offer high accuracy, helping you verify customers quickly and keep honest users moving through your system without friction.
When implemented as part of a robust AML and KYC program, transaction monitoring is an essential defense against money laundering, fraud, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes.
AML screening vs. monitoring: The key differences
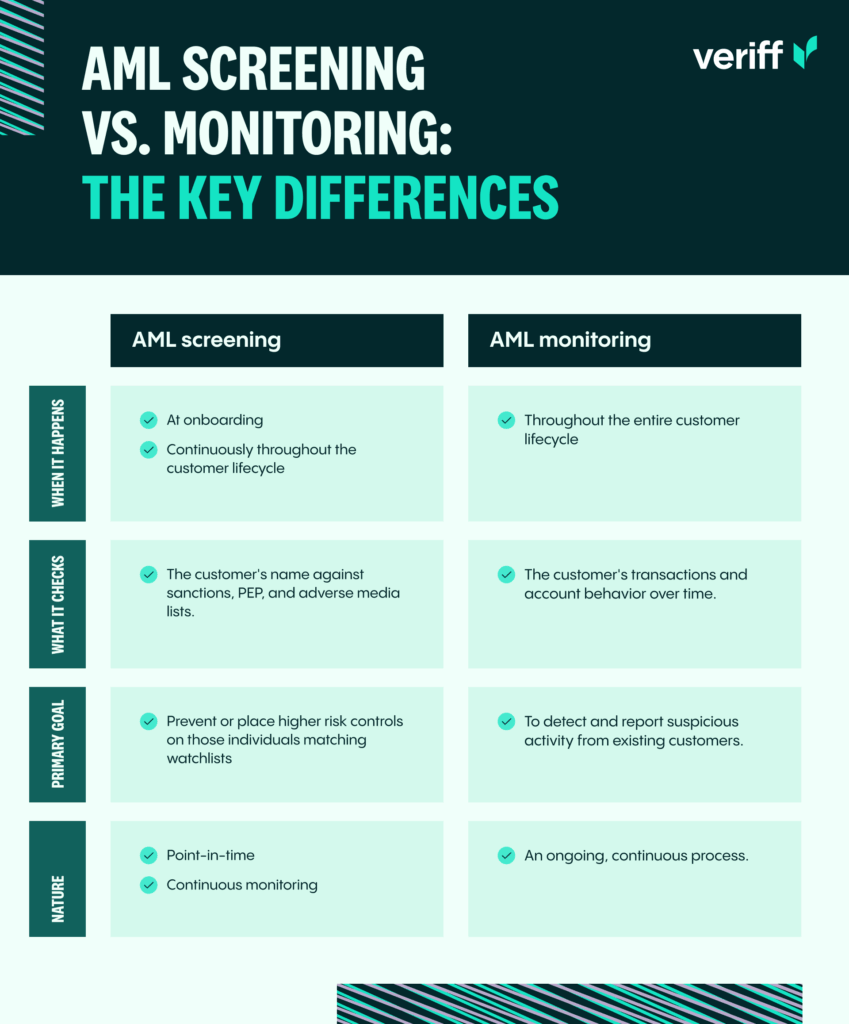
While they serve different functions, screening and monitoring are not mutually exclusive. They are two sides of the same coin, working together to create a comprehensive AML compliance program. Without effective screening, you risk onboarding criminals. Without effective monitoring, you won’t catch them if they start using your platform for illegal purposes.
The rising stakes: Fraud in the modern era
The need for strong AML practices has never been greater. The digital landscape is fraught with risk, and consumers are feeling the impact. Veriff’s Fraud Index Survey 2025 reveals a concerning trend: over 95% of consumers encountered fraudulent or suspicious activity in the past year.
This threat is becoming more advanced. The report found nearly 79% of people have been targeted by AI or deepfake-generated fraud. These technologies allow fraudsters to create highly convincing fake identities and bypass weak security measures, making robust identity verification more critical than ever.
Consumers are aware of the risks and demand action. The Fraud Index shows that 75% of people consider a company’s fraud prevention record before signing up. Furthermore, an overwhelming 97% believe strong security measures, like IDV, are important when signing up for a new financial service.

Uncover the latest fraud trends and benchmarks.
Download your free Report now!
How Veriff strengthens your AML framework
A successful AML program begins with understanding who your customers are, and as regulations evolve worldwide, compliance necessitates a flexible, risk-based approach. As highlighted in Veriff’s AML compliance world tour, financial institutions globally are under increasing pressure to implement robust customer due diligence, stay aligned with country-specific regulations, and respond to the diverse demands of regulators like FinCEN (US), the FCA (UK), AUSTRAC (Australia), and more. This regulatory diversity makes it more important than ever to have adaptable, future-proof tools that support compliance in every market you operate.
Veriff’s advanced identity verification and biometric technology are designed to help businesses navigate this complexity, supporting both AML screening needs across jurisdictions. Our platform empowers organizations to implement a risk-based approach, as recommended by regulators, by enabling flexible customer checks based on risk profiles, geography, and evolving threats.
Fortifying AML screening
Effective AML screening relies on accurate customer data. If a fraudster uses a synthetic or stolen identity, your watch list checks are useless. Veriff’s AI-powered identity verification solution verifies a user’s government-issued ID and uses a biometric selfie to confirm the person is real and matches the document. In some regions, Database Verification checks provide robust identity verification by cross-referencing information against trusted government databases and official registries. This approach not only confirms that an individual’s data matches authoritative records, but also reduces the risk of identity fraud and document forgery, particularly in markets where national ID systems are well-established.This ensures you are screening the genuine individual, not a fake or fraudulent persona.
Veriff further strengthens screening with several powerful features:
- Real-time updates: Get immediate notifications if users match changing watchlists, so you stay current with evolving risks.
- Reduced false positives: Veriff’s solution delivers up to a 70% reduction in false positives and improved alert quality compared to legacy technologies, allowing your team to focus on genuine threats.
- Adverse media screening: Identify negative news or reports efficiently, as Veriff screens millions of articles using AI and labels results in line with FATF categories to reduce noise and catch meaningful risks.
- Daily PEP and sanctions checks: Politically Exposed Person (PEP) profiles are checked for updates daily, while sanctions lists are refreshed every 15 minutes for maximum coverage and compliance.
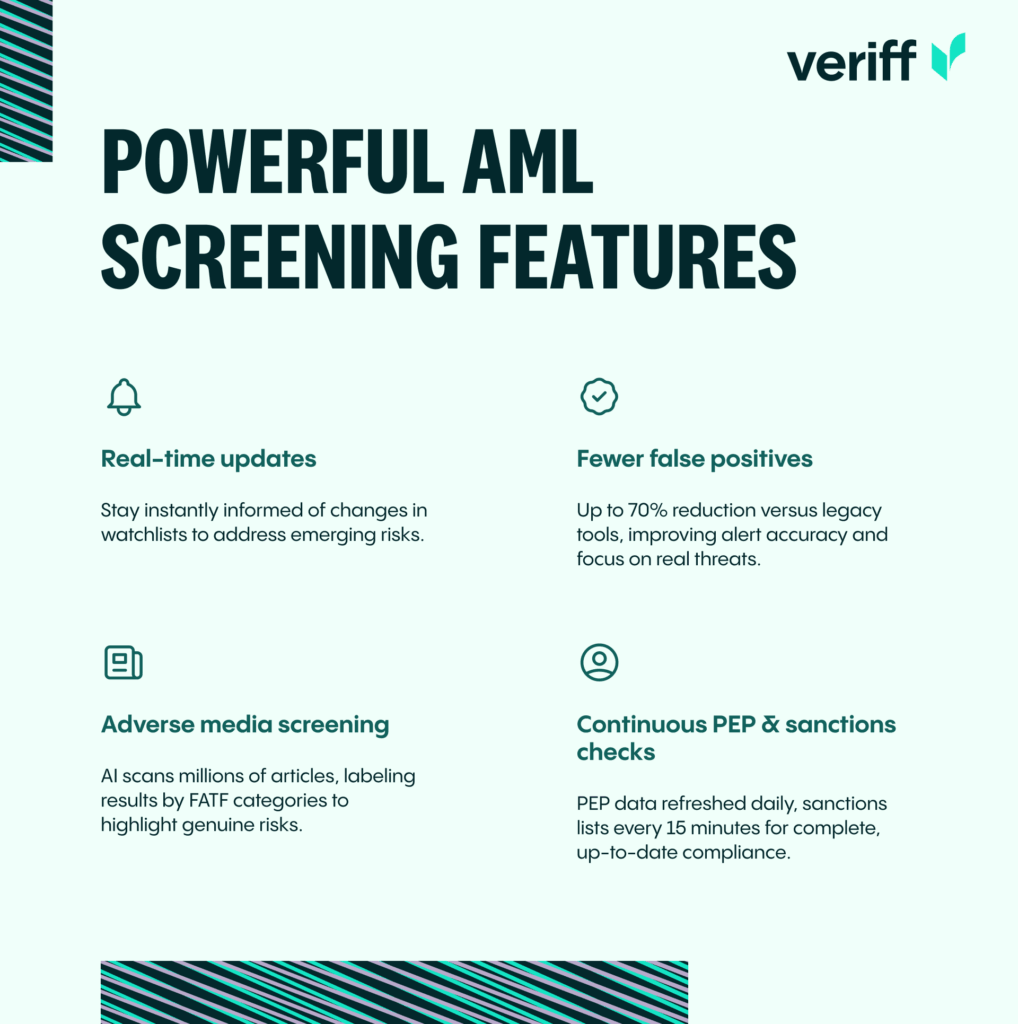
These features work together to create a multi-layered defense against increasingly sophisticated fraud, helping you:
- Prevent onboarding fraud: By ensuring a person is real and present during verification, we block bad actors at the front door.
- Enhance data accuracy: We provide reliable identity data, making your PEP and sanctions screenings more effective.
- Meet KYC requirements: Our robust verification process helps you comply with global regulatory standards.
Supporting AML monitoring
While Veriff is not an AML monitoring platform, our technology provides the foundational trust needed for effective monitoring. By establishing a verified identity baseline at onboarding, you create a reliable profile against which all future activity can be measured.
These robust screening features, such as ongoing match alerts and up-to-date sanctions information—help ensure your ongoing monitoring starts from a solid foundation. When your monitoring system flags a suspicious transaction, our biometric authentication can be used to re-verify the user in real time. This helps confirm that the legitimate account holder is acting, reducing friction for genuine customers while adding a powerful layer of security against account takeovers.
Case in point: How Legitify leverages Veriff to strengthen digital trust
A clear example of how robust identity verification underpins effective AML screening comes from Veriff’s partnership with Legitify, a legal-tech platform simplifying document notarization. In an industry where authenticity and trust are paramount, Legitify integrates Veriff’s AI-powered identity verification to ensure every user is who they claim to be before notarization occurs. This process prevents fraudulent identities from entering the system, much like AML screening stops sanctioned or high-risk individuals at the door. By verifying government-issued IDs and authenticating users through biometric checks, Legitify establishes a trusted identity baseline that supports broader AML compliance efforts. The collaboration highlights how modern IDV tools not only secure onboarding but also enable ongoing monitoring by linking each transaction to a verified, legitimate individua, reducing fraud risk and reinforcing transparency in digital financial ecosystems.
Conclusion: A unified approach to trust and safety
AML screening and monitoring are distinct but interconnected pillars of a strong compliance strategy. Screening acts as the gatekeeper, while monitoring provides ongoing vigilance. In today’s high-risk environment, doing one without the other is like locking your front door, but leaving all the windows open.
As fraud becomes more prevalent and sophisticated, businesses must invest in technology that can establish and maintain trust. Veriff’s identity verification platform provides the anchor of certainty you need to build a resilient AML framework, protect your customers, and grow your business with confidence.

