A Digital Bank is an organisation that can offer banking activities and online services, usually via a mobile app, which was historically only available at a bank branch.
According to the FFIEC (Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council), e-banking is the “automated delivery of new and traditional banking products and services directly to customers through electronic, interactive communication channels.” The ‘banking products and services' that this relates to are:
- Money Deposits, Withdrawals, and Transfers
- Checking/Saving Account Management
- Applying for Financial Products
- Loan Management
- Paying bills/invoices
- Account Services
In essence, a digital bank should be able to provide all the banking functions that have traditionally been carried out at bank head offices, branch offices and via bank cards such as a debit card at ATM machines.
The earliest forms of digital banking experience and digital platforms can be traced back to the introduction of ATM machines and cards which were launched in the 1960s. When the internet and digital networks became widely available in the 1990s, online banking suddenly emerged as a viable option, with what we know as modern digital banking starting to appear.
The advancement of smartphones in the millennium then opened the door for even more advanced transactions. These days it is thought that 76 percent of individuals use online banks regularly as of 2020.
What is a digital bank account?
A digital bank account is simply an account with a digital bank, where all normal banking services - whether related to debit cards, credit cards, current account or anything else - are available online, without the need to visit a physical branch.
Different types of digital banks
There are many different types of digital banks (as well as types of digital banking channels) such as ‘Challenger Banks', ‘Neobanks', ‘Beta Banks' and ‘Non-banks'. For the purpose of this blog, we're going to focus on the two biggest categories – ‘Challenger Banks' and ‘Neobanks'.
Challenger Banks
Essentially, challenger banks are Fintechs that have their own banking licenses which means that they can offer the traditional banking services in a flexible way.
can all be categorised as challenger banks and are direct competitors of traditional banks across the world.
Another stand-out feature of challenger banks is that they tend to streamline the retail banking process by leveraging new and innovative technology. In addition to this, challenger banks do have a physical presence, although this is usually quite small.
It is estimated that there are 100 challenger banks in operation globally today.
Neo Banks
The main difference between challenger banks and neobanks is that neobanks do not hold a banking license but instead rely on a partner bank. This means that they're unable to offer some banking services.
Neobanks are completely digital banks that have no physical presence. They reach out to customers via mobile banking apps and online platforms and often offer more user-friendly interfaces and fee-free digital services. Neobanks also tend to focus on a specific customer area such as SMEs.
A global report on neobanks from Business Insider Intelligence estimates that there were 39 million neobank users as of the end of 2019.
The 7 advantages of digital banking
There are many advantages of modern digital banking solutions with neo- and challenger banks alike. The online banking industry is so diverse and fluid that new benefits and digital banking services seem to be emerging all the time.
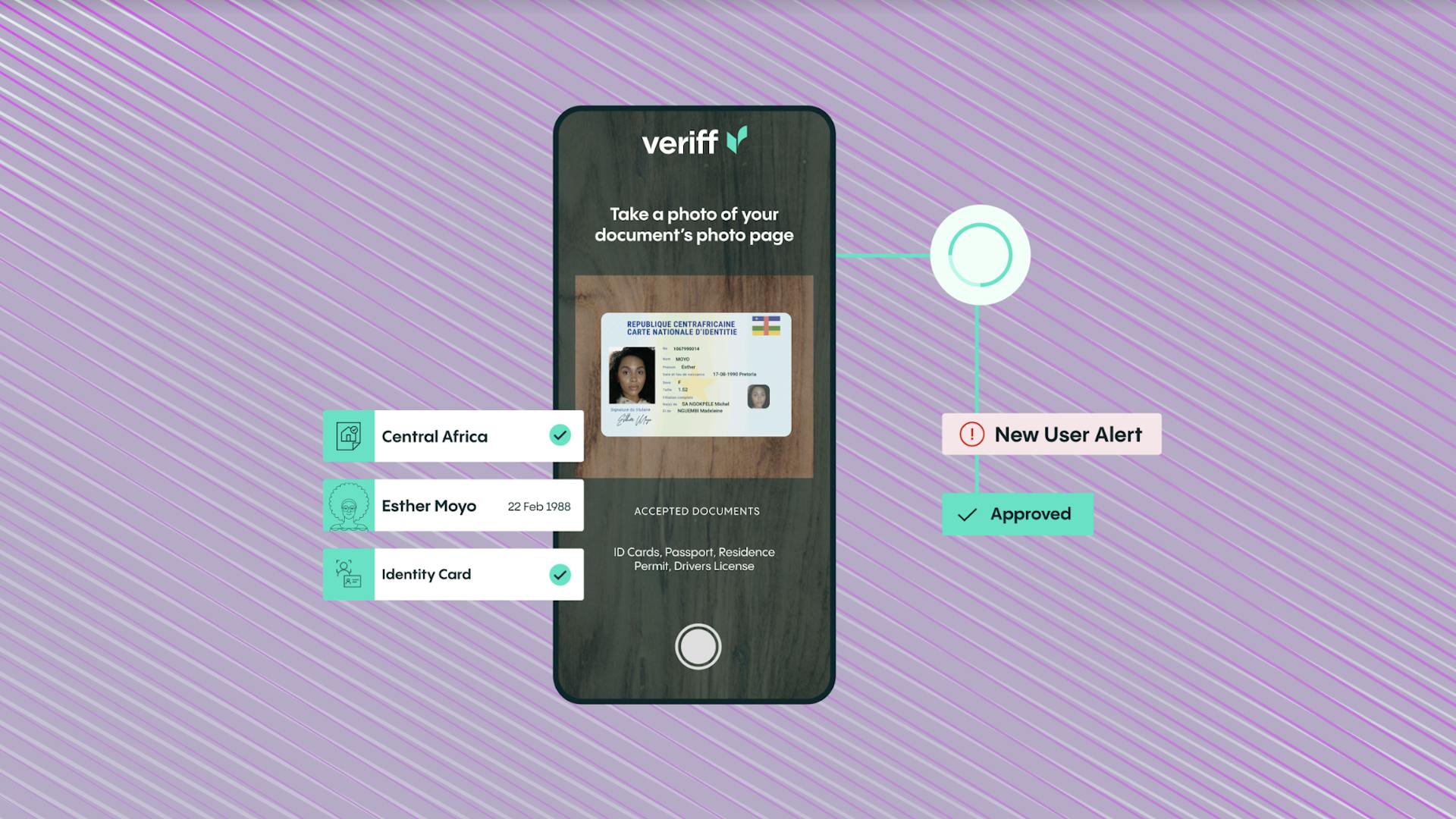
- Simplified onboarding process: Digital Banks can onboard new customers so much more easily than traditional banks. It is usually a paperless process with documents like proof of ID, employment and address uploaded via smartphones and verified quickly and efficiently. Identity verification is a hugely important aspect of this and can be done extremely efficiently through partnerships with companies like Veriff . The fact that most online banking accounts can now be set-up via just a smartphone is a huge leap from the long queues and tedious waits that banking customers used to face.
- Constant access: The digitization of banking means that customers can now access their accounts 24/7 and carry out all manner of transactions with a few touches of a button. This means that the customer experience and satisfaction level is miles better than it was previously and many people now feel much more in control of their banking than ever before.
- Cost savings: Interestingly, this is a benefit for the bank that then cascades down to the customers as well. Automated services, the lack of physical branches and less employees means that neobanks and challenger banks have considerably fewer costs than traditional banks. These savings can be passed down to customers as reduced charges and services that are much more competitively priced.
- Security-focused: Customer and data security is a hugely important aspect of any type of banking and it certainly seems to be something that digital banks are leading on. Traditional banks have been known to be quite slow to adopt new security measures, whereas digital banks see it as a fundamental part of their system.
- Accuracy: Paper processing that is a necessity at traditional banks is naturally at risk of human error. Alongside this, traditional banks often see errors due to ineffectual integration between branch interactions and back office requirements. Neobanks and challenger banks cut out these risk factors and their processes are often more accurate as a result.
- Agility: Digital banks are less cumbersome entities than traditional banks and are often headed by more forward-thinking and innovative leadership. This means that they are often more flexible in adopting new technology and being able to quickly offer new services to banking customers.
- New services: Speaking of new services, many digital banks have been able to offer a range of new services to customers in recent years. This includes real-time spending notifications, 24/7 in-app support, free payments when travelling, regular spending reports, spending projections and partnerships with other financial apps and services.
Safety of digital banking
There are some people out there who are still suspicious of the safety of digital-only banks and mobile banking, lamenting the loss of physical bank branches and questioning the digitization of such important financial services.
However, the reality could not be more different. Digital-only banks have always made security one of their main priorities and as such, have adopted much more innovative and technologically secure protocols than many traditional banks.
The most high tech methods of in-app and payment authentication are often sought after by digital banks and they provide them to customers via partners such as Veriff . This includes practices such as:
- Identity verification
- Facial recognition
- Fingerprint scanning
- Voice recognition
When it comes to regulatory banking bodies, most digital banks and digital banking solutions are usually covered by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and/or the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), which adds another level of security, bringing added peace of mind to already happy customers.


